Blockchain - what is it in simple words?
A Simple Guide for the Newest of Beginners.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a database that is not centrally located in one place, but distributed across many computers. The most important task of a blockchain is to securely document digital transactions. The technology has become famous thanks to cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ethereum.
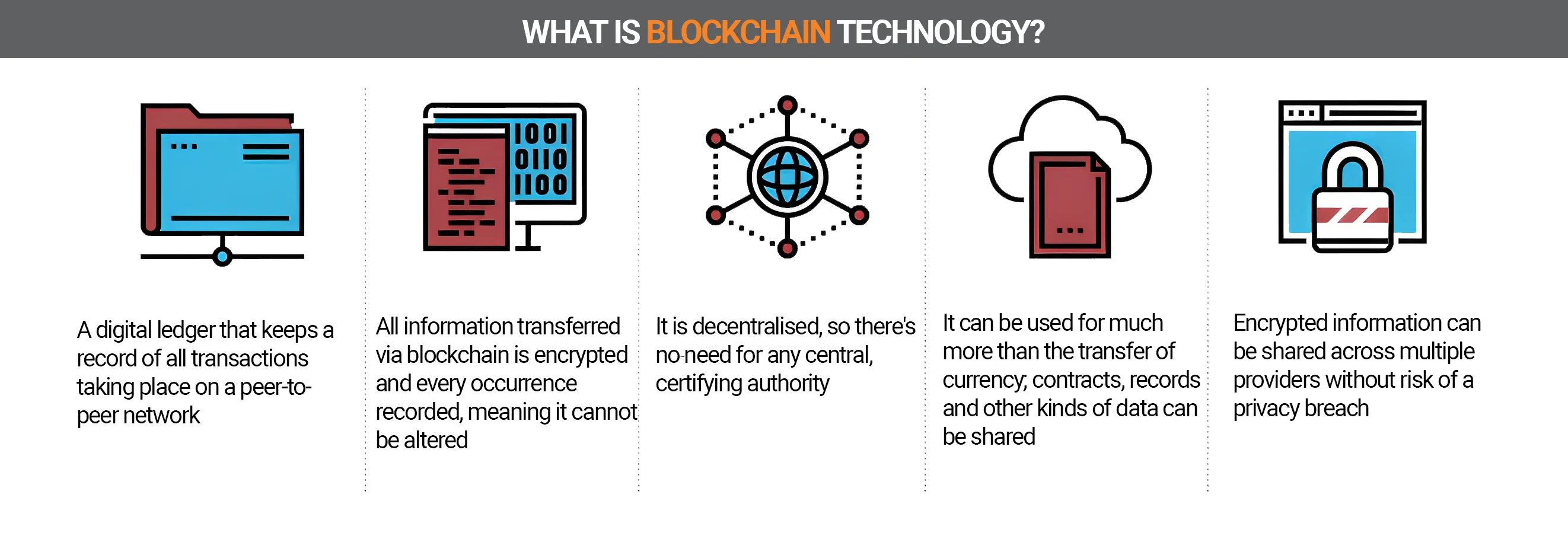
Simply put, a blockchain is a decentralized or distributed database (also: distributed ledger). This means that it does not reside with one person or organization, but exists as a complete copy on a large number of computers.
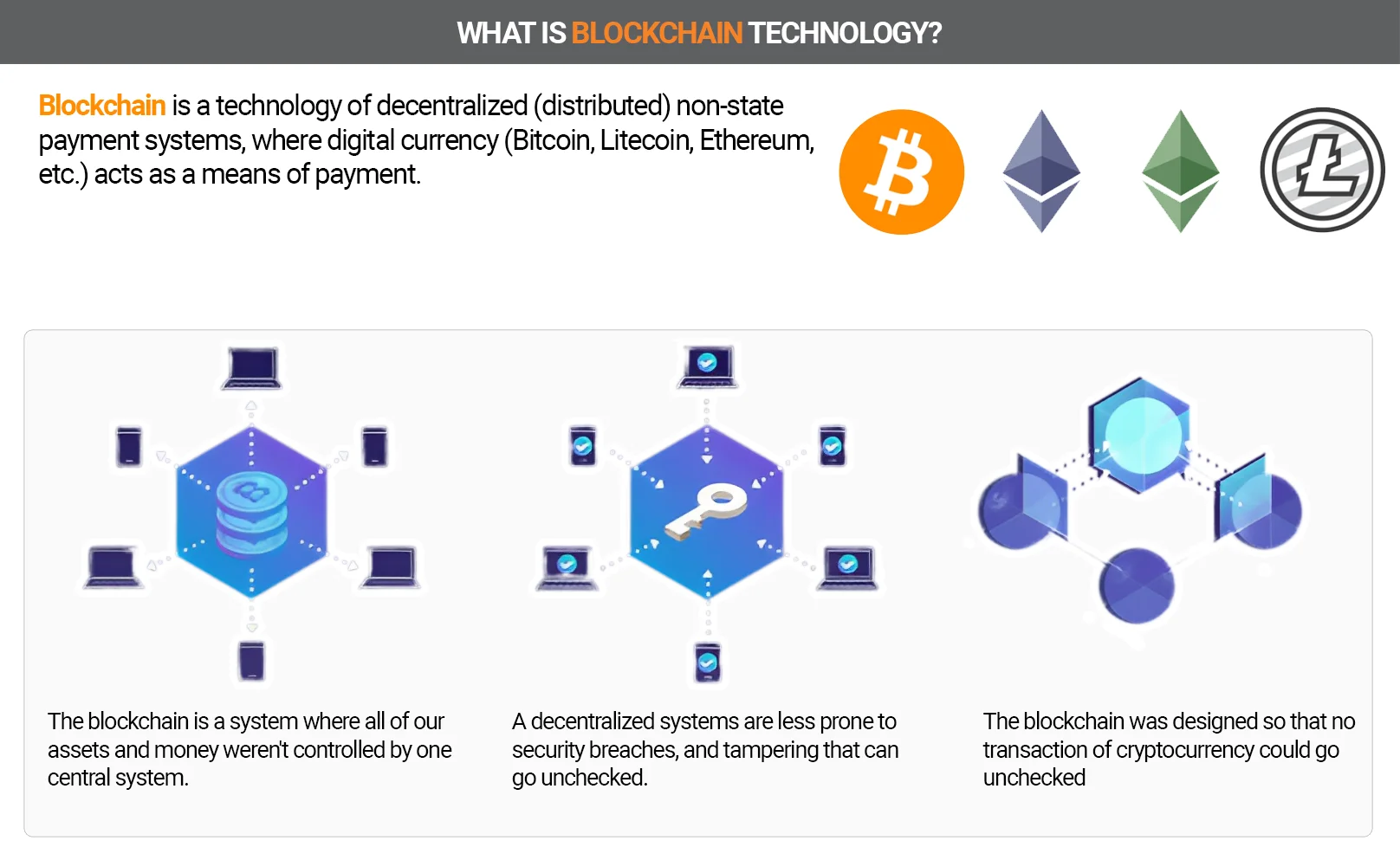
Blockchain was created as a cash book for the virtual currency Bitcoin, in which all users should be able to view all transactions. This technology is now being used for other cryptocurrencies as well.
Important terms and clear explanations
- bitcoin
- Digital money designed for decentralized payments, that is, transactions without intermediaries such as banks.
- Cryptocurrency
- Bitcoin is also called a cryptocurrency. The Bitcoin payment system uses cryptographic methods to store the information it contains.
- Mining
- The process of mining cryptocurrency using the power of computers. They solve complex tasks by validating the blockchain network. At the same time, a new block of bitcoins is found, for which miners receive a reward.
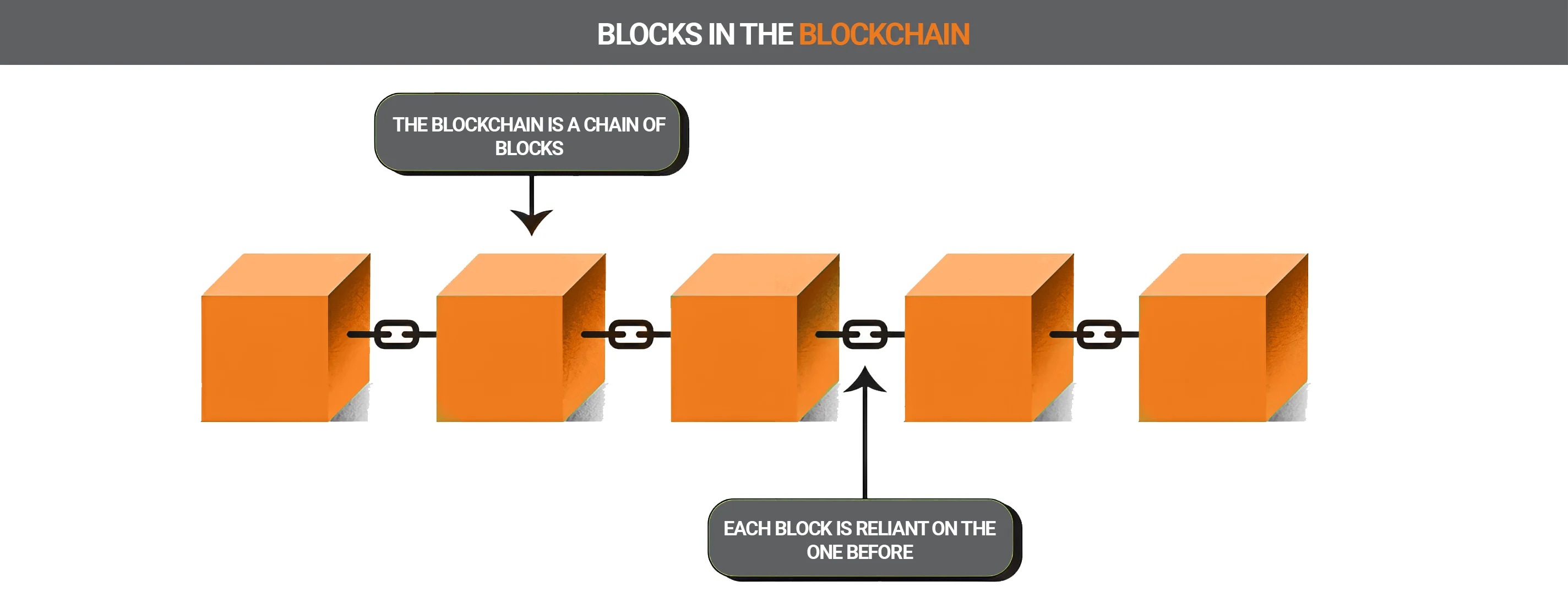
As the name suggests, a blockchain is a aggregation of blocks of data. The easiest way to illustrate this approach is with an example. To do this, we use the Bitcoin cryptocurrency:
Simply put, a block of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum can be compared to an Excel spreadsheet that has the following structure:
| User A (sender) | User B (recipient) | transaction amount |
|---|---|---|
| bc1ql2qw7ujlpn27hat32nklptsyytff30ys8wpj96 | bc1qhs3gptkxem5y7yaq2yg0un2m8hae6wt87gkx4n | 0.0518814 BTC |
| bc1qrpp7g75sx3ejclvsfdw2uahzchtyu7vumkuadu | bc1q4s0vsp6gpc2aqt0cvd703hxy5jv93d76mra2mf | 0.0002813 BTC |
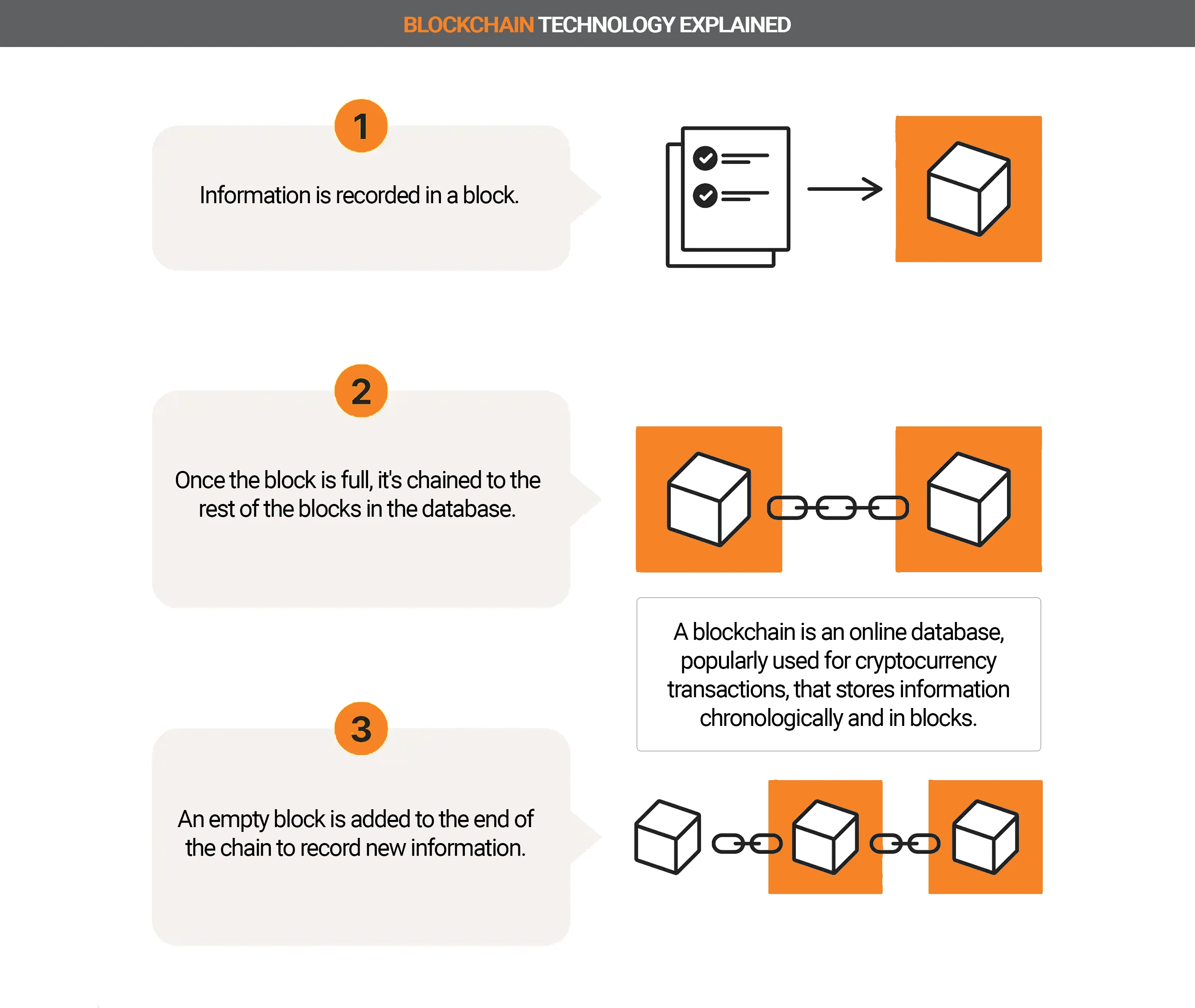
The contents of the first two columns are the anonymous addresses (hash) of the sender and recipient of the corresponding transaction. With each transaction, the table (block) is supplemented with the next row. When a certain number of lines (size) is reached, the block is closed, sealed and filed. Then the next block starts.
Over time, numerous blocks are created that line up: the blockchain. The more blocks in the blockchain network, the higher the security. These blocks are created by miners.
The big difference between a regular database and a blockchain is decentralized storage. The technology works with a network of computers and servers that store each individual block in parallel.
Don Tapscott, Executive Chairman of the Blockchain Research Institute, is one of the world’s leading authorities on the impact of technology on business and society. 1
How the technology works
Let’s explain using Bitcoin as an example. Think of blockchain as a ledger. Users of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency initiate transactions by buying, selling or paying with currency. As with an account, these movements must be recorded so that others can understand the transactions.
As a result, no one loses sight of how much Bitcoin has been bought and sold. Therefore, the computers involved create a block for transactions containing all the necessary information. The block is attached to the blockchain - the registry, expanding it. Computers encrypt the block using a complex algorithm.
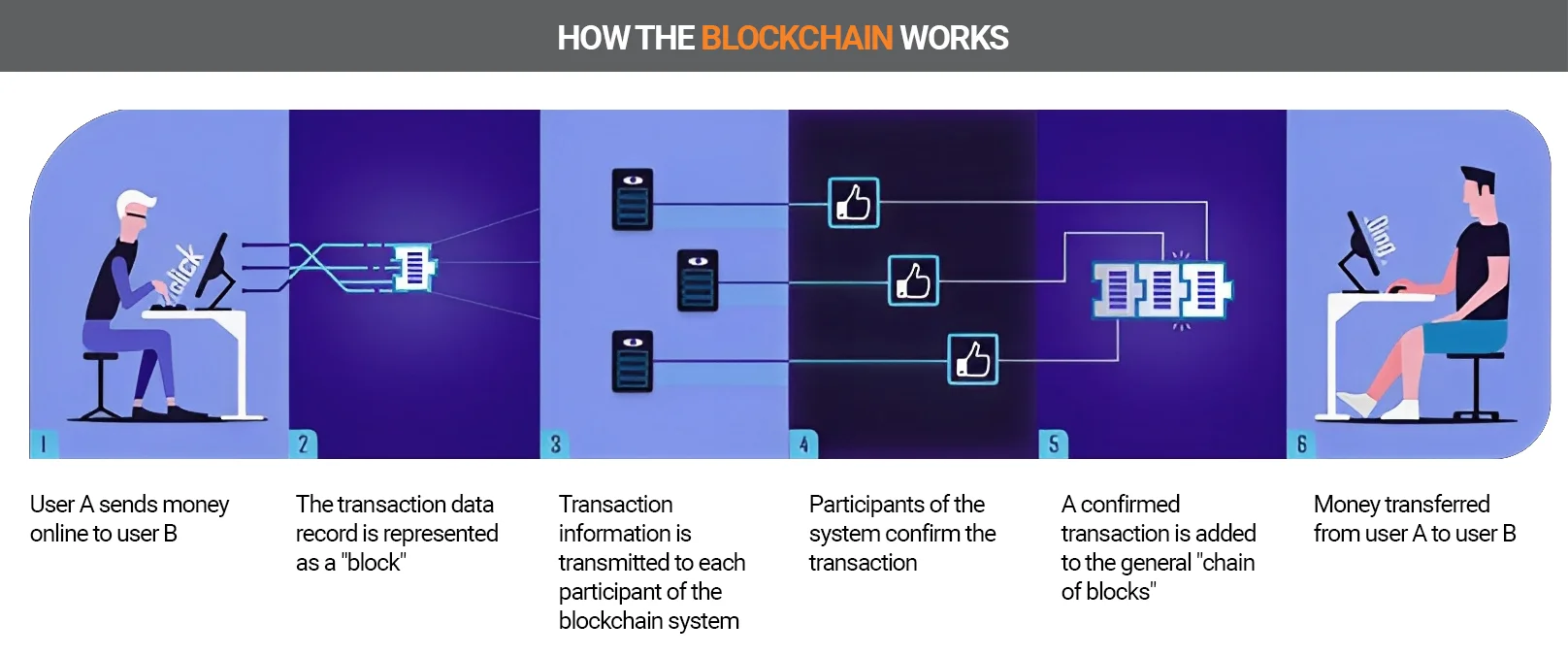
Here is an example of how the technology works:
- Buyer A buys bitcoins from buyer B.
- The blockchain network recognizes the booking and combines it with other cryptocurrency transactions into one block.
- All computers participating in the network now calculate the encryption algorithm.
- After the algorithm is generated, the computers coordinate and add the encrypted block to the block chain.
- All computers participating in the network keep the same block.
- Transaction completed.
Application, implementation in business
Blockchain technology is the modern and best form of doing business. It removes layers of “bureaucracy” and friction. Blockchain also eliminates the need for businesses that provide services related to checking and certifying goods, guarantees, and registering/recording a transaction in a public registry.
This means that all related jobs (accountants, sales representatives, lawyers, and other office administration workers) and businesses that have traditionally served these needs are a thing of the past.2
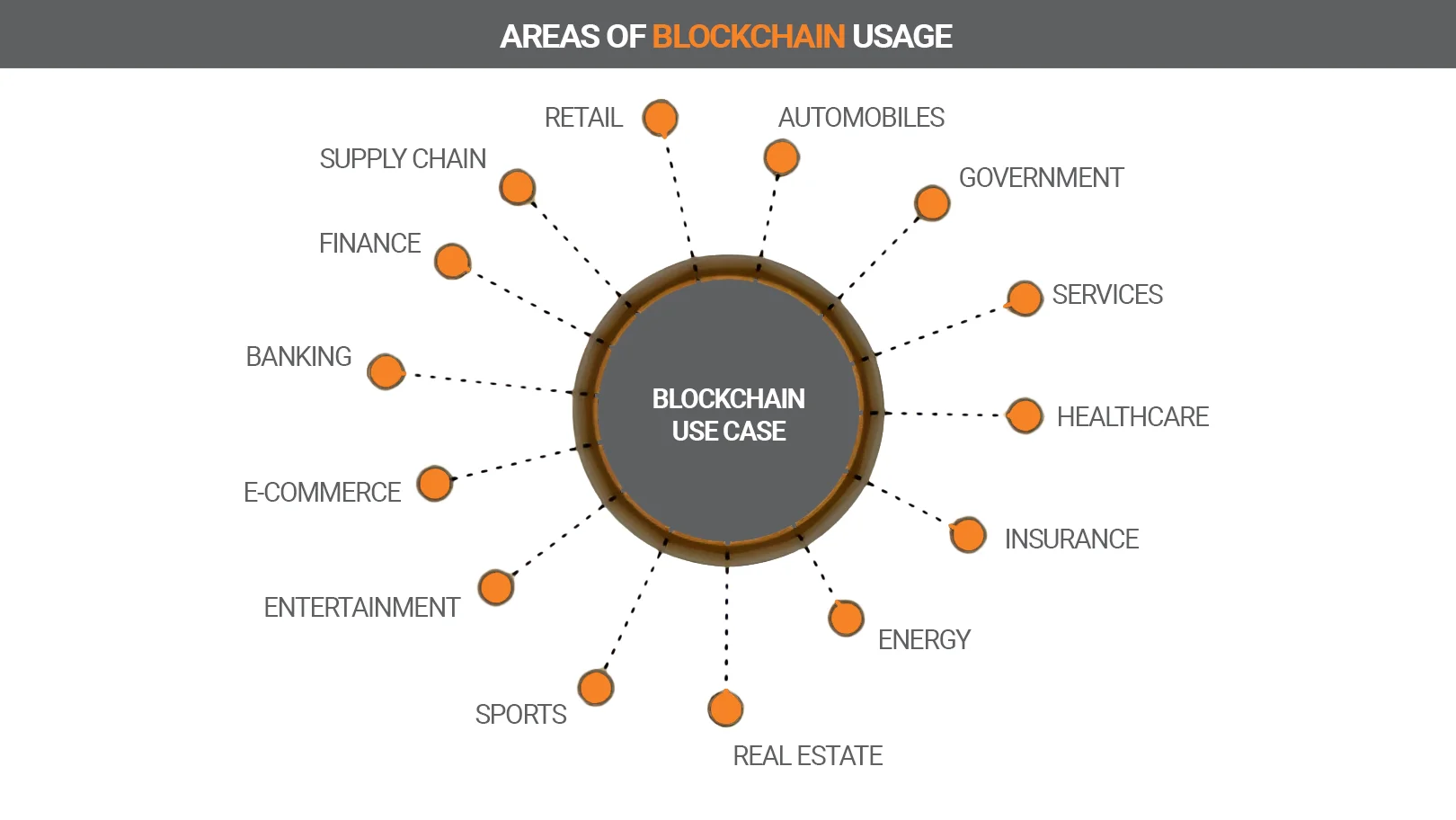
Blockchain can be applied to the following business areas:
- Retail
- Transport
- Logistics
- Management
- Finance
- Services
- Banking
- Healthcare
- E-commerce
- Insurance
- Entertainment
- Energy
- Sports
- Real estate
Which business will kill blockchain
Blockchain is needed where the speed and reliability of data transfer is important - that is, in almost all areas of life: when concluding smart contracts for the supply of goods, buying and registering real estate, logistics. This technology enhances the trust, security, transparency, and traceability of data exchanged across a business network.
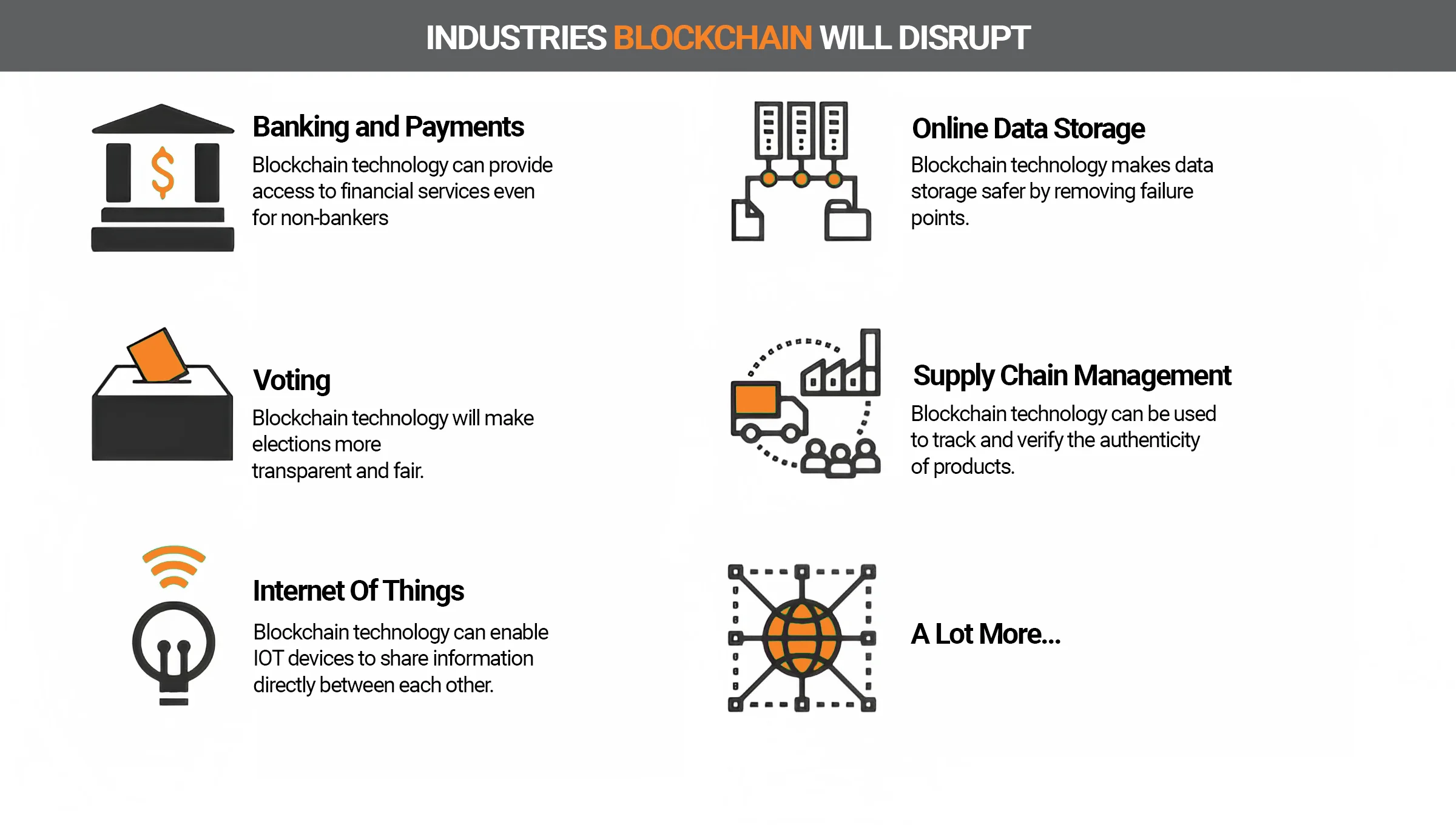
Banking and payments
One of the most famous use cases of blockchain is financial transactions. First of all, cryptocurrencies illustrate how this technology can be used in the financial world.
How is blockchain better than traditional banks?
It uses encryption. This is done using the hash function and protects data from hacking and manipulation.
In the process of using the blockchain, individual transactions are verified and distributed among the so-called nodes (miners, validators, network participants). This results in a high level of data consistency and a particularly high degree of transparency. These properties are the basis for banking operations.
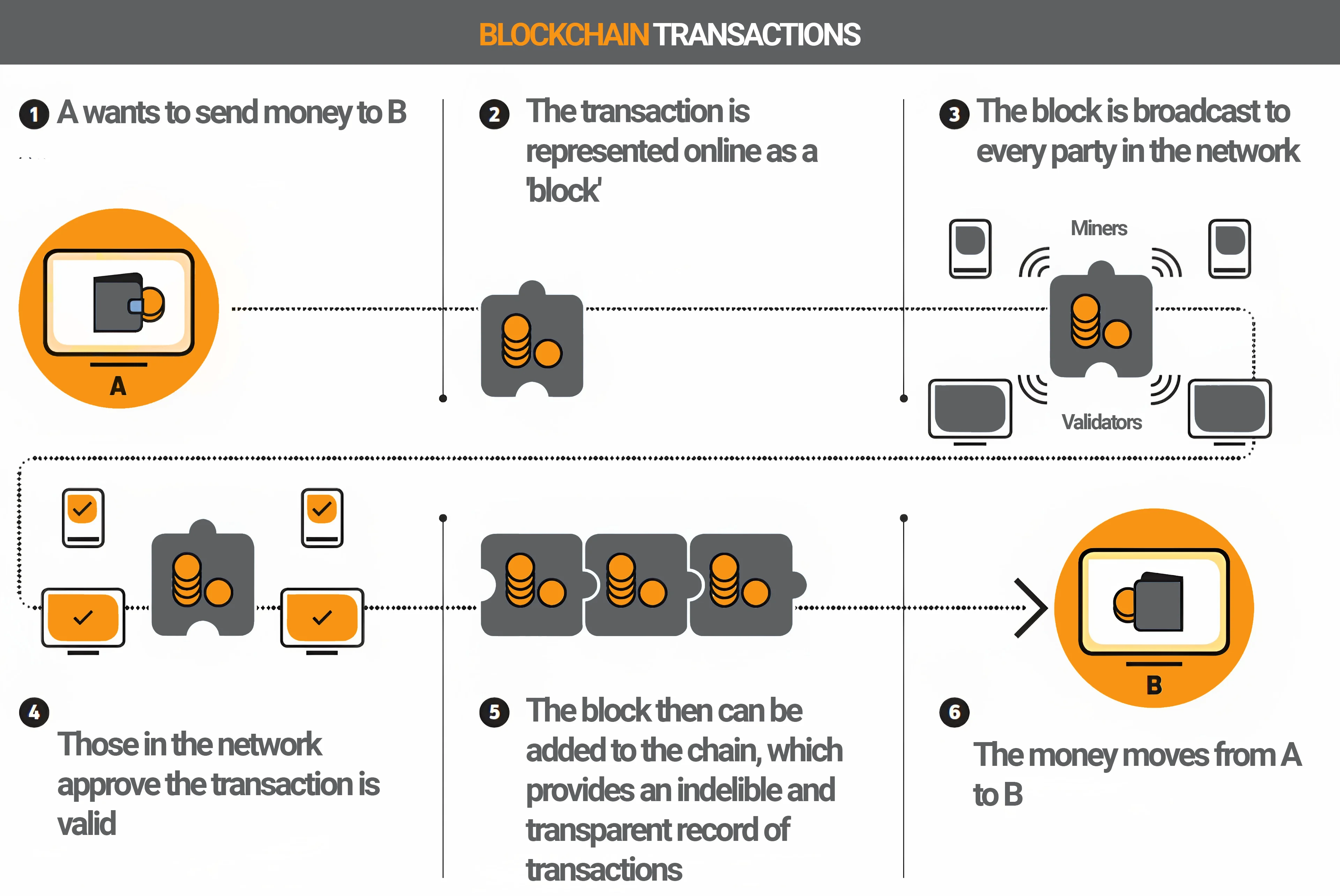
This principle opens up interesting applications for international payments. Since verification takes place internally, intermediaries can be eliminated and transaction costs can be reduced. The absence of intermediaries also ensures faster transaction speeds.
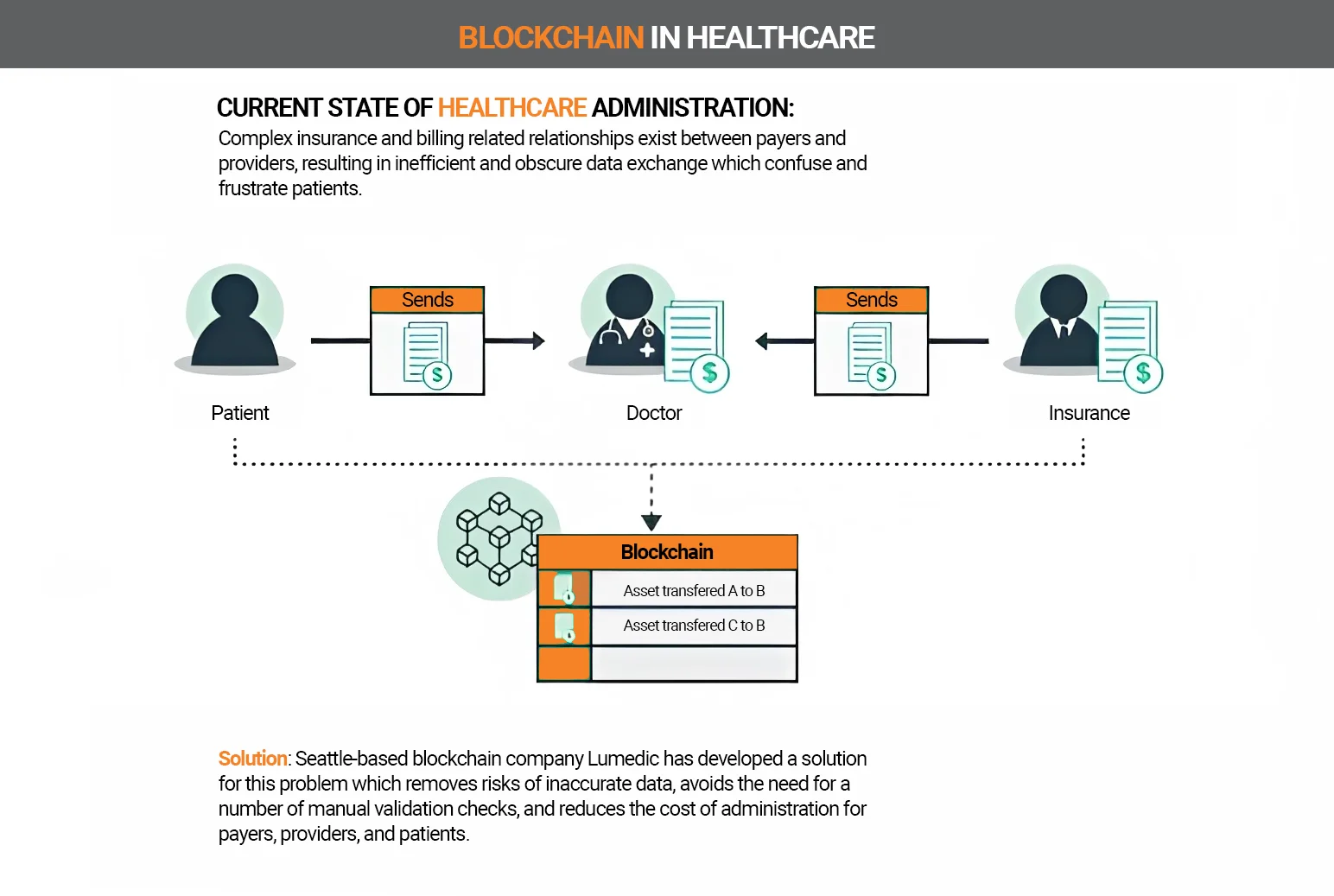
Healthcare
The healthcare sector is also showing that blockchain can definitely offer benefits. It can be configured so that only selected users have access to stored data (assets).
In particular, personal documents such as patient records, medical reports, and disease progression can be stored on the blockchain. Access to this data is provided only to selected users who were previously recognized as the owner of the data.
Identity and personal data management
Identification is a complex task in some business areas. However, with the help of blockchain technology, people’s identities can be identified more safely and quickly than before.
This is based on extensive databases that allow identification and verification. In particular, existing identity documents — driver’s licenses, passports, and ID cards — can be securely implemented digitally. Manipulation would also be virtually impossible.
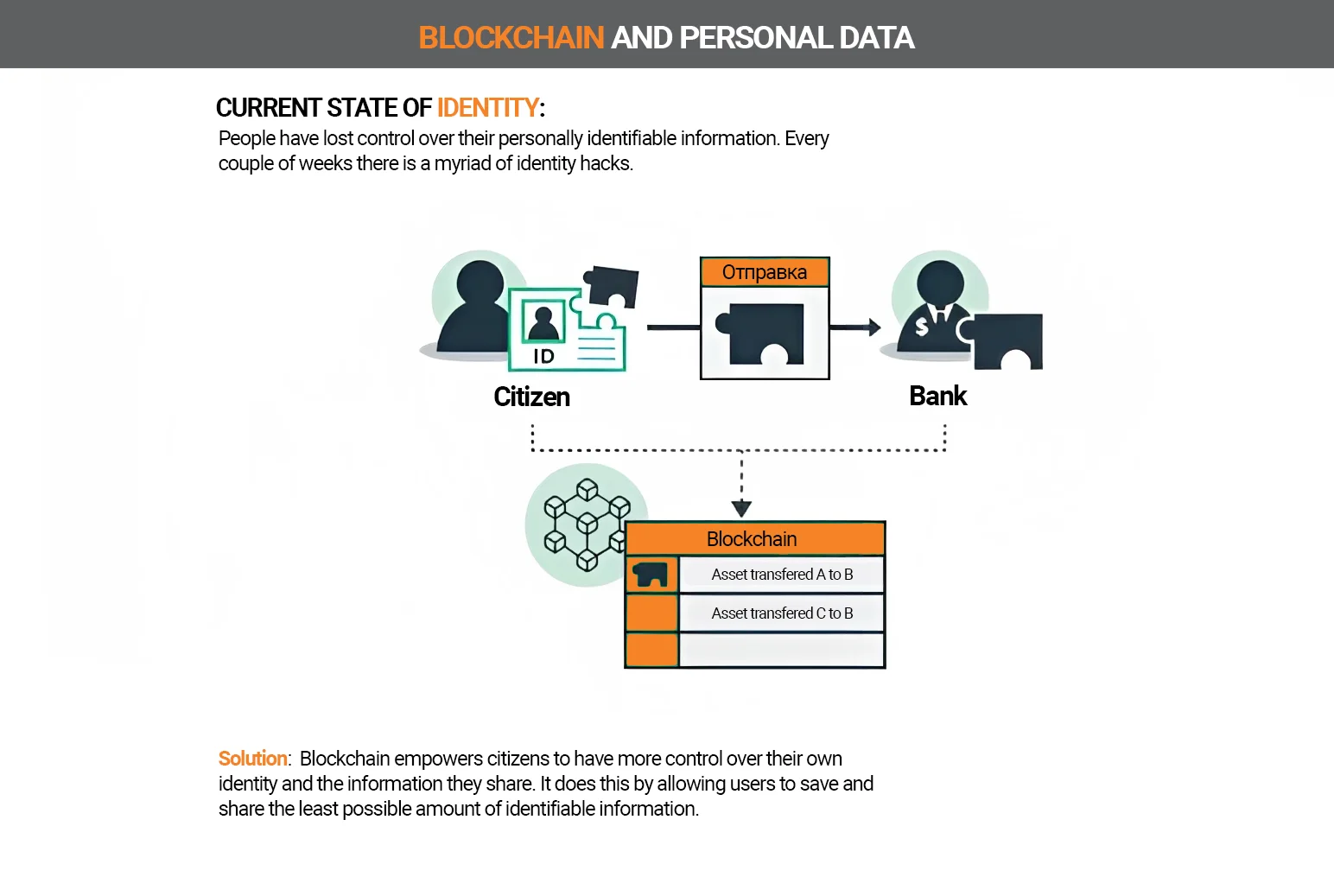
Data leakage will also be prevented as the data is stored in a decentralized manner.
Insurance
Modern blockchains offer the possibility of developing smart contracts. These are intelligent computer scripts that automatically initiate transactions on the blockchain.
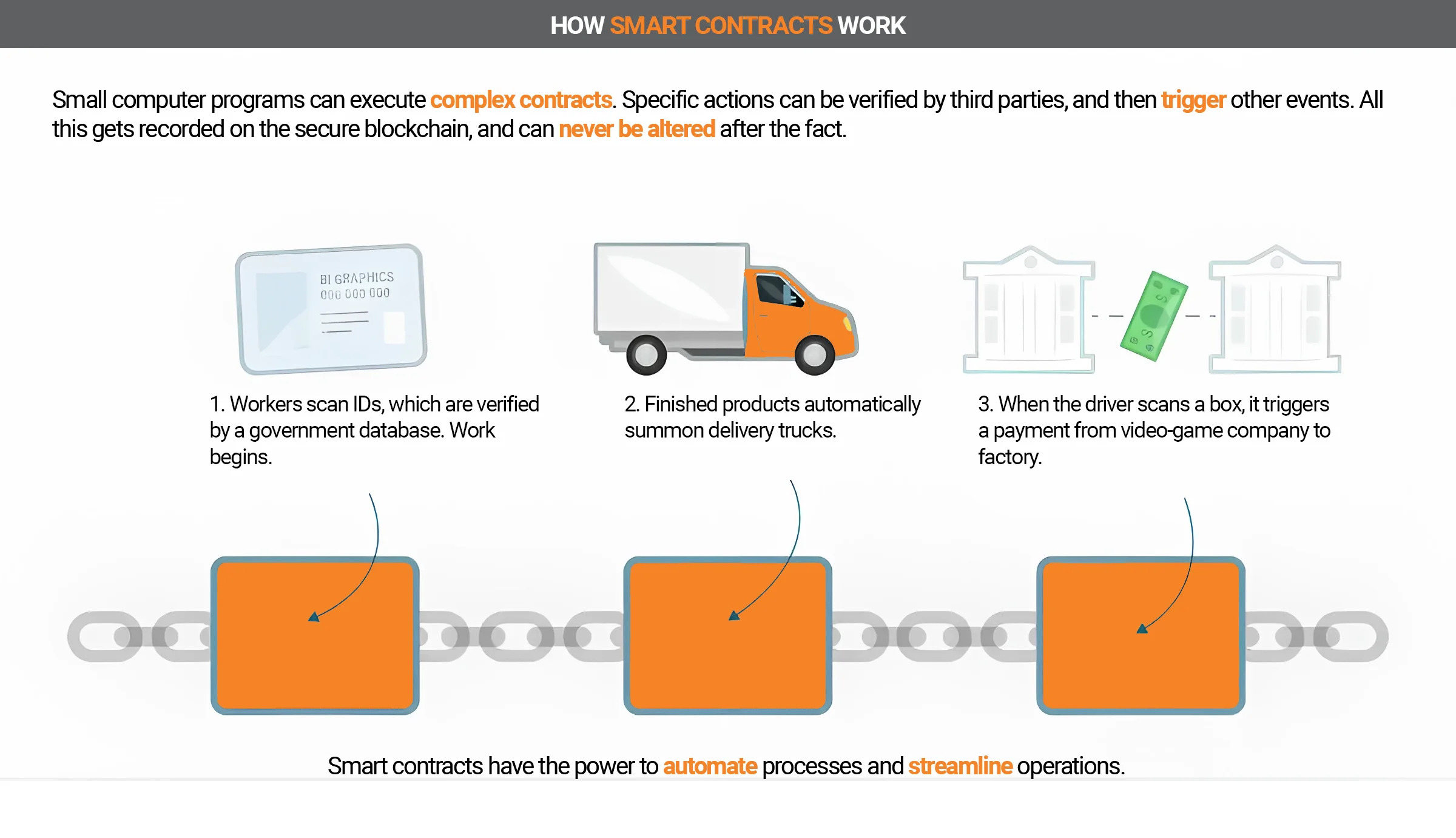
The results are predetermined in the contract and depend on the actions of the parties involved in the smart contract. When both parties fulfill their obligations, the smart contract will know what action to take next. 3
For insurance companies, smart contracts offer great added value because, above all, the processing of claims for damages or insurance payments can be displayed automatically and securely.
Supply chain
Logistics advantages can be obtained by creating simpler contracts and constantly tracking the relevant goods.
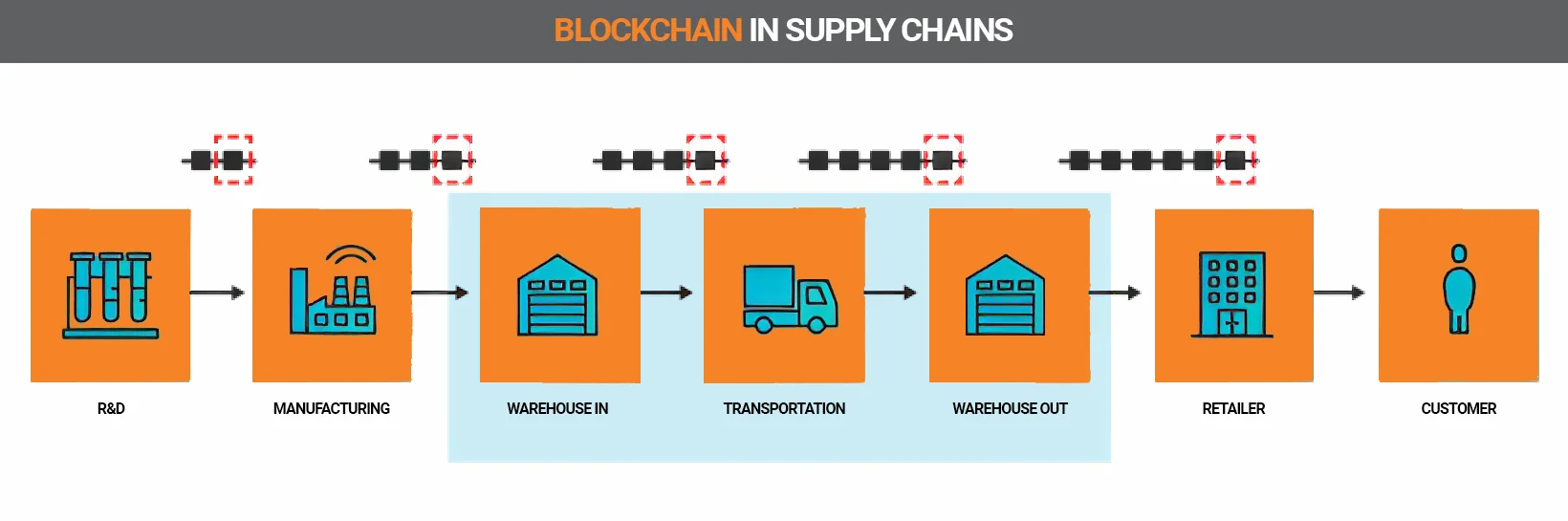
Thus, the food supply chain will be completely transparently documented from the point of origin to the final supermarket. This is where the advantage of distributed data processing offered by blockchain becomes apparent.
For example, blockchain could be used to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, from the point of origin to the point of sale. This would allow all stakeholders to see where the goods are at any given time and make sure that they are being handled properly. Additionally, blockchain could be used to verify the authenticity of goods, ensuring that only certified, safe products are being sold.4
Manufacturing
The option of distribution of access rights also plays a key role in manufacturing. In addition, the technology can document the ownership of an item and is suitable for use in this area.
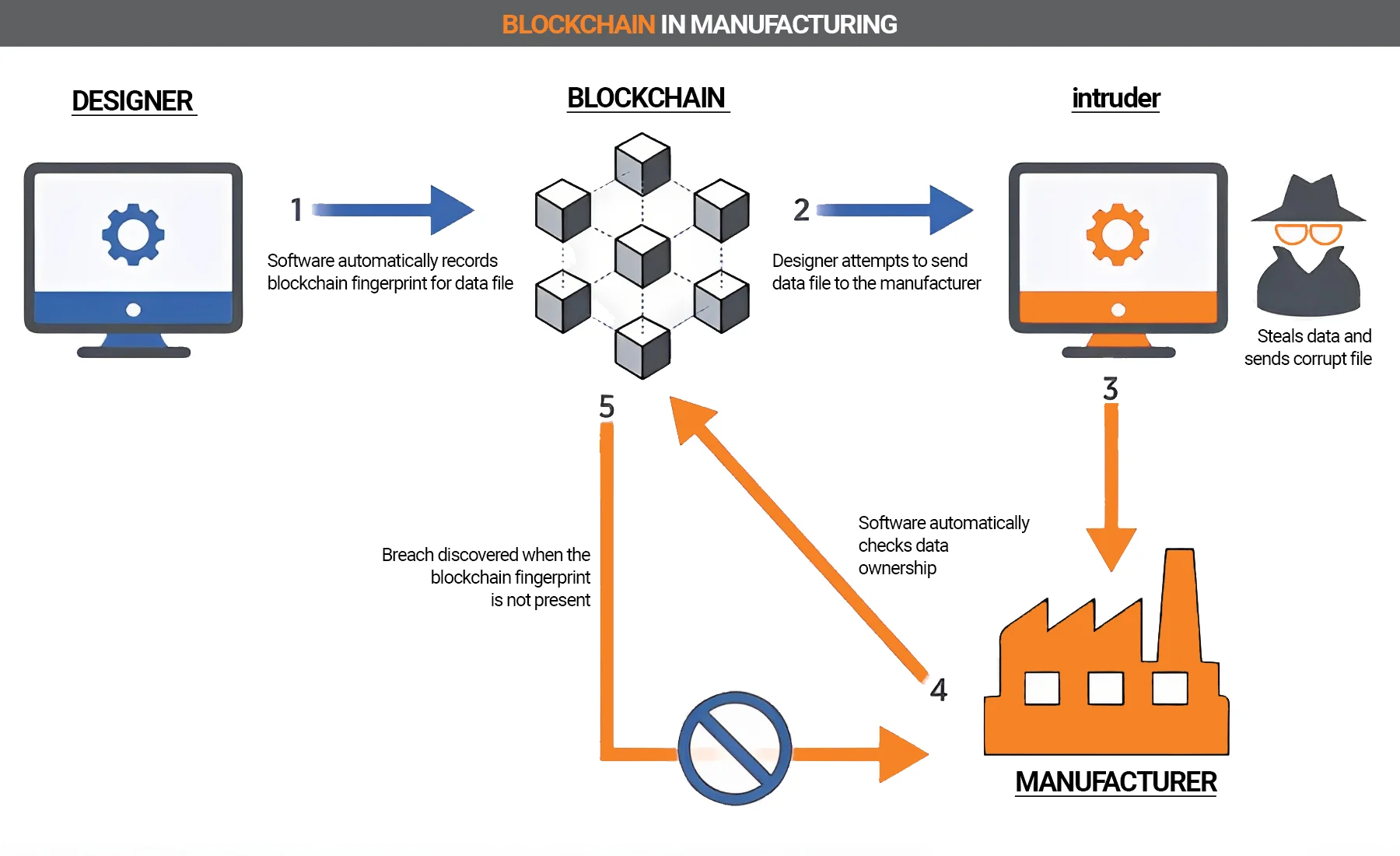
With distributed ledger technology, it will be possible to use the vehicle/equipment when needed and pay directly for the service used.
Energy
The energy market is also undergoing constant changes. Blockchain technology is preparing to increase the transparency of this market by making transactions traceable.
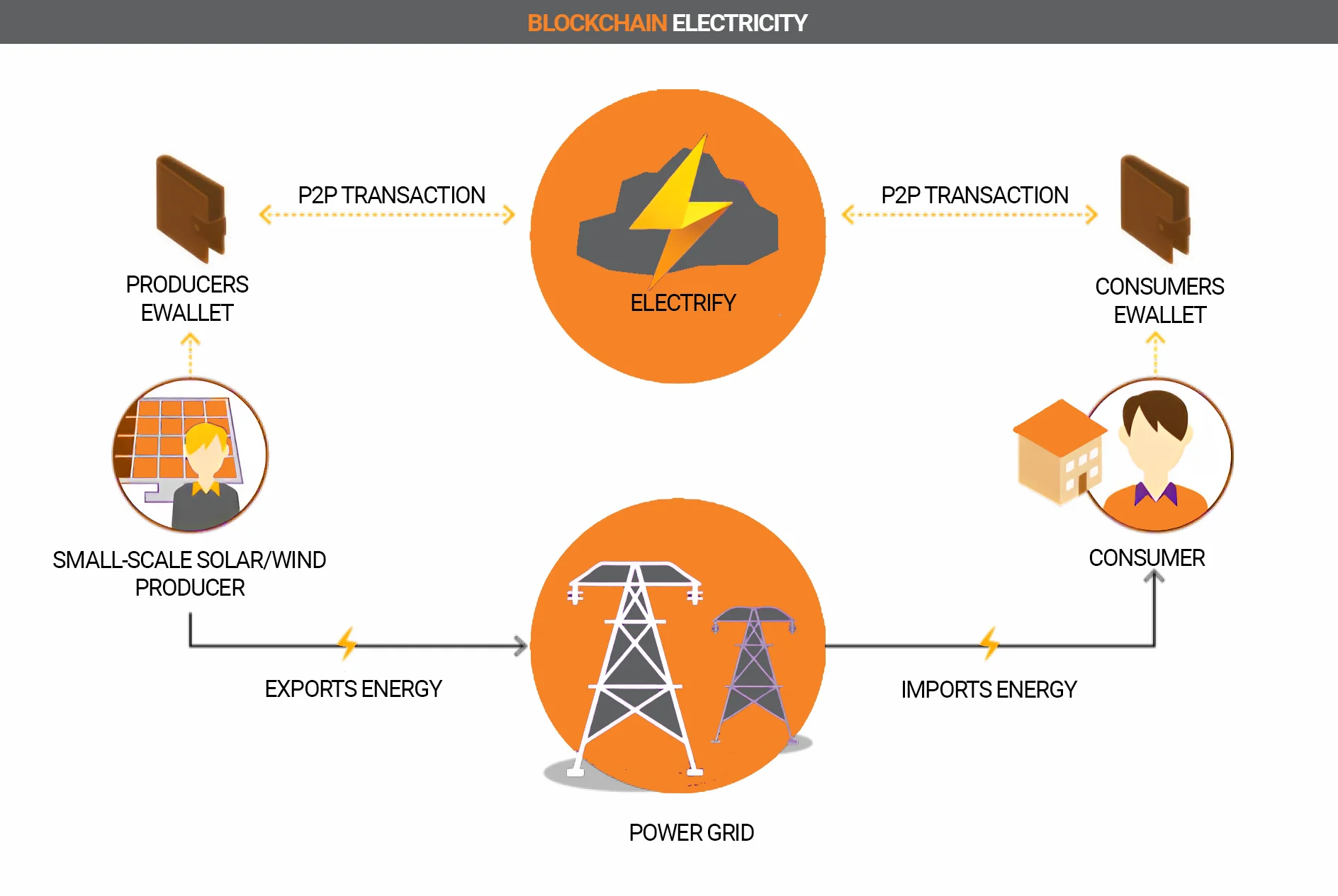
For example, the billing of private solar systems can be optimized in this way. Such positive regulation could accelerate the announced energy transition.
Within the framework of electromobility, billing for electronic charging stations can also be implemented in this way and the actual payment process can be ensured.
Voting system
Blockchain technology can also be used in online elections. The base system will be considered a neutral space. Voters could take part in elections without fear of manipulation.
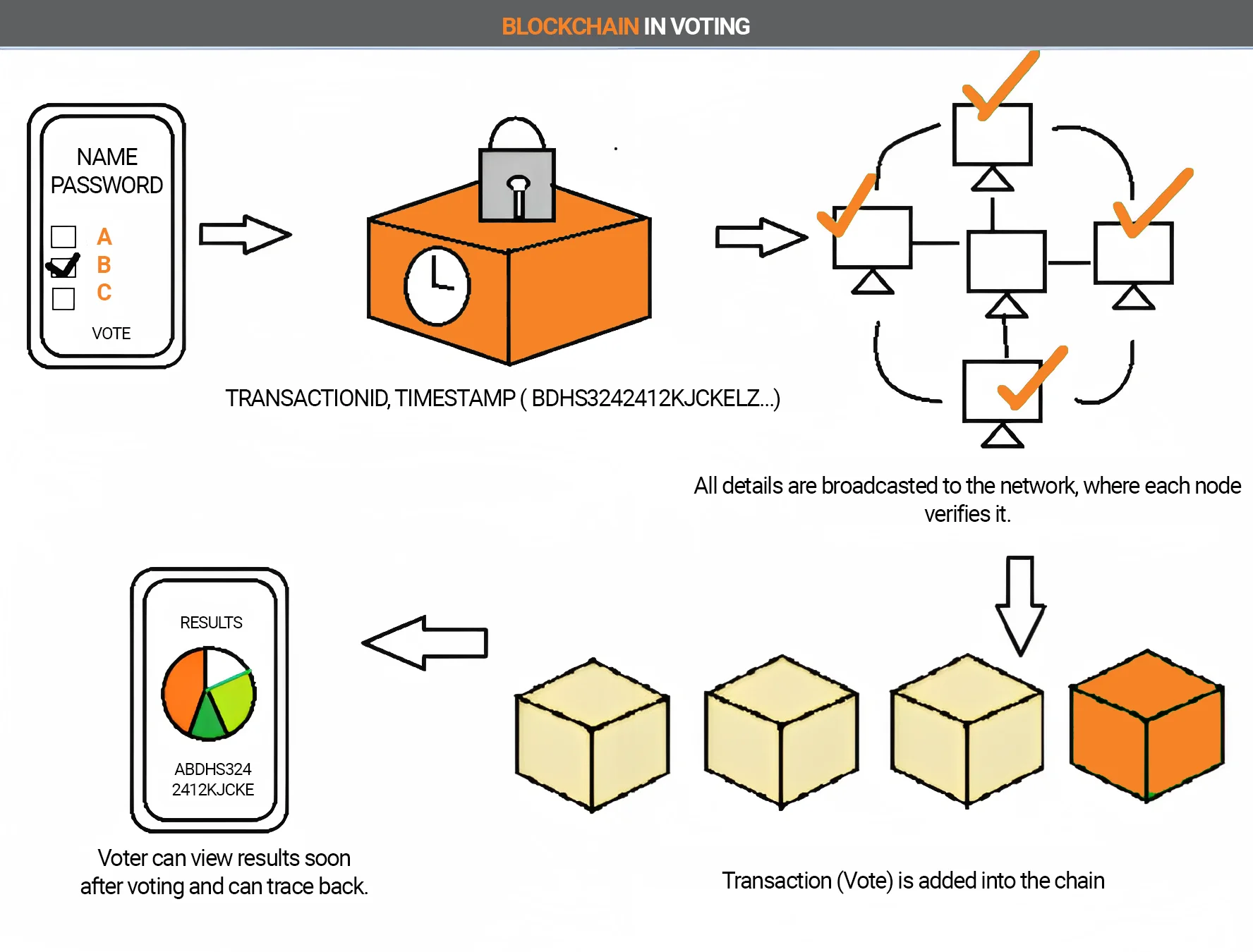
In this way, each voter can also keep track of their vote and check if it was counted correctly. Faking or changing the voice is also not possible.
Certification
Educational qualifications such as references or certificates are the backbone of professional life and some people rely on fakes to get certified by a well-known specialized institution.
Using the blockchain, institutions, universities and technical colleges are able to issue diplomas and certificates that cannot be counterfeited. They will be protected by a private key and recognized internationally.
Thus, official certification and sending of original documents will be excluded.
WIRED challenged political scientist and blockchain researcher Bettina Warburg to explain blockchain technology to 5 different people; a child, a teen, a college student, a grad student, and an expert.5
Advantages
Top 10 Benefits of Blockchain Technology:
- Transparency.
- Reducing transaction costs.
- Flexibility.
- Faster transaction settlement, decentralization, user-controlled network.
- Distributed architecture.
- Openness.
- Automated operations.
- Efficiency, auditability, traceability.
- Safety.
- Worldwide implementation.
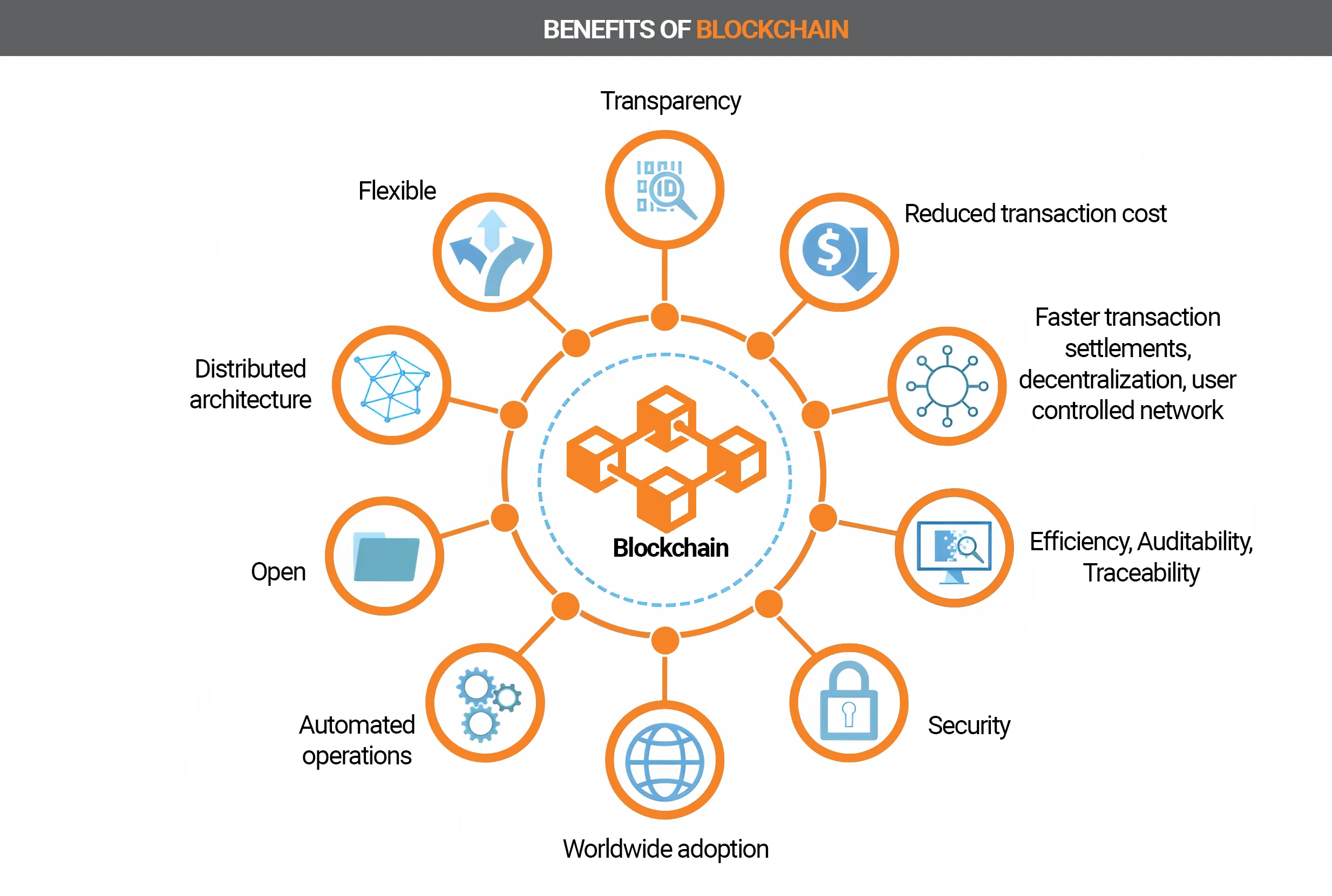
Thus, the blockchain can guarantee the accuracy and security of data records and create the need for third-party services.6
Disadvantages
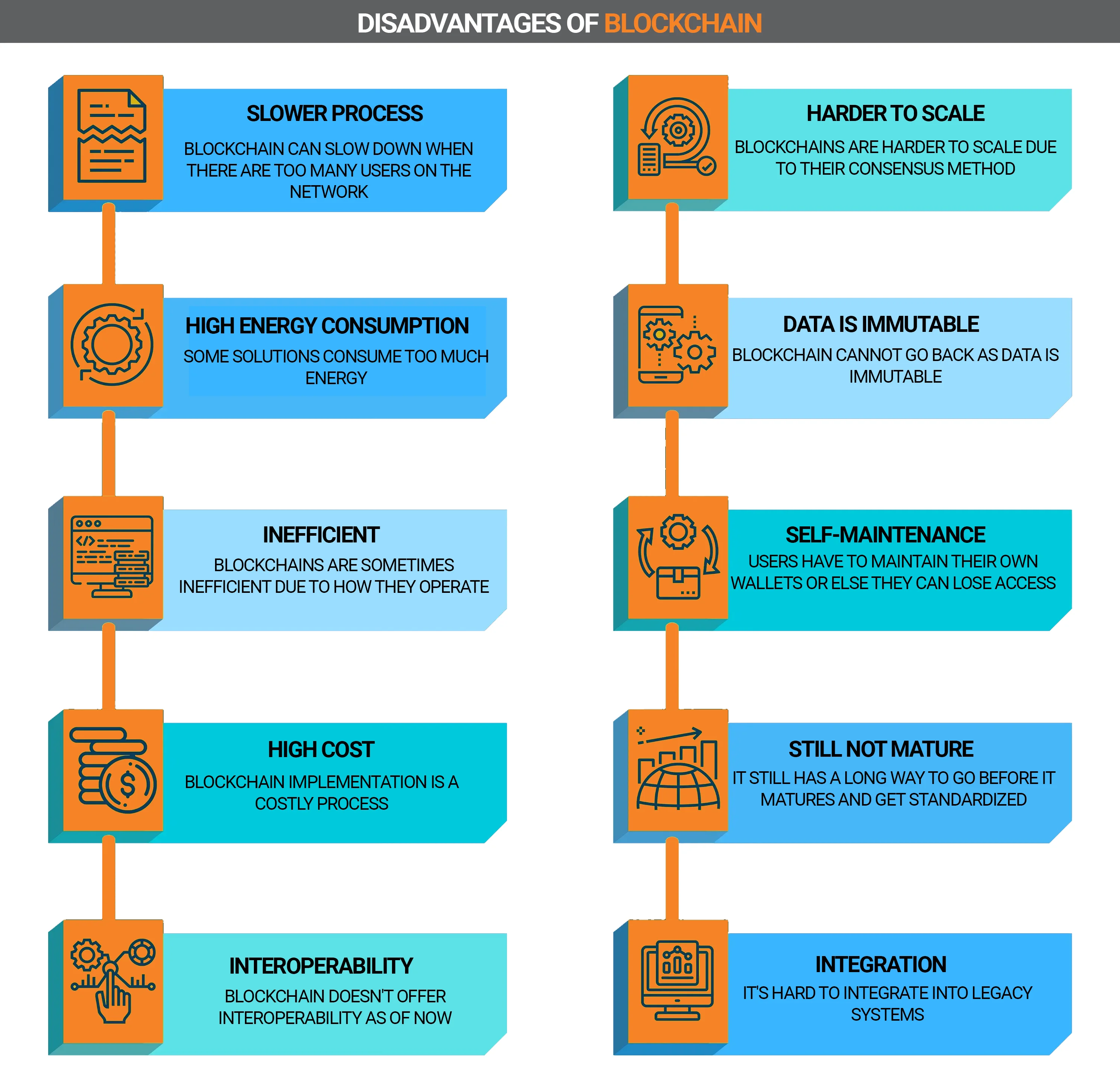
Top 10 disadvantages of blockchain technology:
- Low performance.
- The problem of scalability.
- Some blockchain solutions consume too much energy.
- It is difficult to correct an error or make adjustments - the data is unchanged.
- Not completely safe.
- High cost and implementation difficulties.
- Expert knowledge required.
- Users must keep private keys.
- Young technology, little implementation experience.
- Low compatibility with old databases.
Conclusions
Blockchain technology still has potential. However, the required computing power, high power consumption are the subject of criticism. PTherefore, numerous developers are working on improvements.
So far, the decentralized database has impressed with its transparency, speed, and security.
The technology can be used in all areas of business. Above all, transparency, decentralization and security play an important role. Many companies are already discovering the possibilities of the technology and developing their own products based on the blockchain. Many experts see great future potential in this technology, so developments in the coming years are likely to be particularly interesting.
Question answer
Validators, like miners in a Proof-of-Work (PoW) network, are network nodes that operate on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains, and also verify blocks of transactions in the blockchain.
Blockchain data is stored in a decentralized public ledger. Ledger data is stored in chunks called blocks, which are linked to each other using cryptography.
